Content

Brainyard delivers data-driven insights and expert advice to help businesses discover, interpret and act on emerging opportunities and trends. If you are deaf, hard of hearing, or have a speech disability, please dial to access telecommunications relay services. There are two main strategies businesses commonly use to achieve this. In our illustrative example, our company has the following financial data as of Year 0. Free Financial Modeling Guide A Complete Guide to Financial Modeling This resource is designed to be the best free guide to financial modeling! Based in Atlanta, Georgia, W D Adkins has been writing professionally since 2008.
Your bookkeeping team imports bank statements, categorizes transactions, and prepares financial statements every month. Because these items aren’t part of the company’s core activities and may occur infrequently, it’s helpful to separate them from the business’ results of operations. If you calculate OER for your business, compare it to industry benchmarks.
Employee travel, marketing campaigns and repair of key equipment are all examples of operational activities. An operating expense is an expense that is related to a business’s core operations. https://www.bookstime.com/ are the first expenses shown on a company’s profit and loss statement. The amount left over after operating expenses have been deducted from gross revenue is known as operating income. By contrast, a non-operating expense is an expense incurred by a business that is unrelated to the business’s core operations. The most common types of non-operating expenses are interest charges or other costs of borrowing and losses on the disposal of assets.
Non-operating expenses are incurred outside of everyday business activities and related to financing or investing activities. Examples of non-operating costs include obsolete inventory charges, lawsuit settlements, losses on investments, damages caused by natural disasters and fires, restructuring costs and interest expenses. Any costs related to making goods or delivering services are also not part of OpEx. Operating costs are the result of a company’s operating activities, or activities directly related to selling products or services to customers.
If a company is trying to invest in its future and wants to be most efficient with its long-term capital, it might be better for it to invest in CapEx rather than OpEx. Alternatively, if a company wants to preserve capital and maintain flexibility, it might be better off incurring OpEx instead. Earnings before interest and taxes is an indicator of a company’s profitability and is calculated as revenue minus expenses, excluding taxes and interest. A cash flow statement is a financial statement that provides aggregate data regarding all cash inflows and outflows a company receives. Peggy James is a CPA with over 9 years of experience in accounting and finance, including corporate, nonprofit, and personal finance environments. She most recently worked at Duke University and is the owner of Peggy James, CPA, PLLC, serving small businesses, nonprofits, solopreneurs, freelancers, and individuals.
Adkins holds master’s degrees in history and sociology from Georgia State University. He became a member of the Society of Professional Journalists in 2009. They are not fully tax-deductible in the year they are purchased; rather, they are deductible over time. Child Advocacy Centers stress coordination of investigative and intervention services by bringing together professionals and agencies as a multi-disciplinary team …
If Operating Expenses are too high, then it cuts into profit margins, making it difficult for a business to grow, or perhaps even to cause a business to fail. A business needs to find the right balance between ensuring they are engaging in all necessary business operations without having operating expenses be too high. See operating expenses examples and learn how to find operating expenses on an income statement. It’s crucial to understand operating expenses as how you deal with them differs. That’s in terms of tax and accountancy, and as compared to other costs. The two most notable different kinds of expenses are capital and non-operating expenses.
Capital expenditures are funds used by a company to acquire or upgrade physical assets such as property, buildings, or equipment. Capital expenditures, or CapEx, are costs that often yield long-term benefit to a company. Operating expenditures, or OpEx, are costs that often have a much shorter-term benefit. OpEx is usually classified as costs that will yield benefits to a company within the next 12 months but do not extend beyond that. Though they may tracked separately internally, each type of cost may have its own budget, forecast, long-term plan, and financial manager to oversee the planning and reporting of each.
In throughput accounting, the cost accounting aspect of the theory of constraints , operating expense is the money spent turning inventory into throughput. In TOC, operating expense is limited to costs that vary strictly with the quantity produced, like raw materials and purchased components. Everything else is a fixed cost, including labour (unless there is a regular and significant chance that workers will not work a full-time week when they report on their first day). It is important to distinguish between operating expenses and capital expenditures as the two are treated differently for accounting purposes. CAPEX include costs related to acquiring or upgrading capital assets such as property, plant, and equipment. These expenses, unlike operating expenses, can be capitalized for tax purposes. In general, businesses are allowed to write off operating expenses for the year in which the expenses were incurred; alternatively, businesses must capitalize capital expenses/costs.
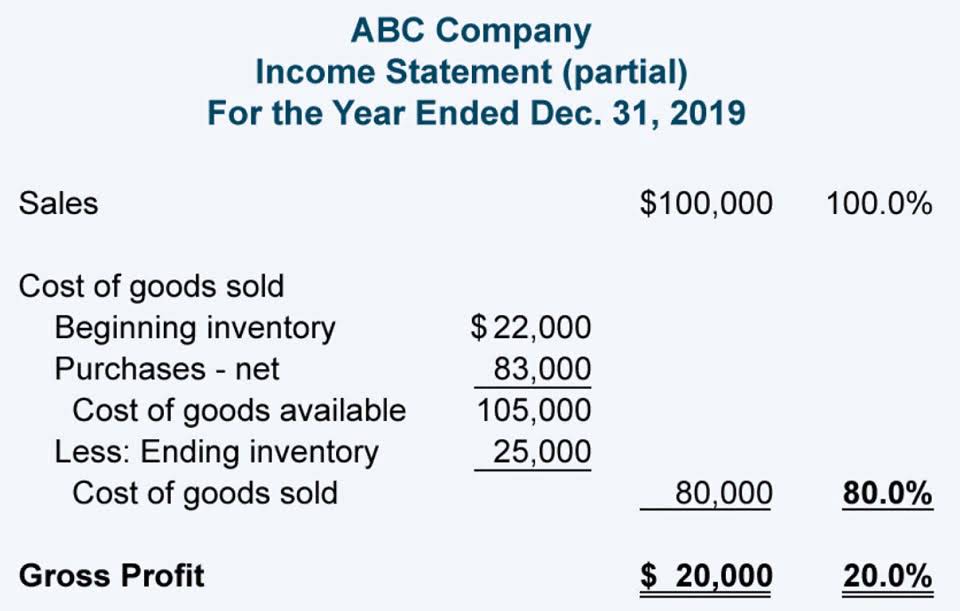
In accounting, a company’s gross profit is shown as the first line item on the profit and loss statement. Deducting the operating expenses from the gross income gives the operating income. Some business owners don’t have an income statement for their business, or their income statement doesn’t separate expenses into cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and non-operating expenses. In this case, you can still get a sense of how much it costs to run your business. Simply review your general ledger or expense report and identify any recurring costs that aren’t the direct labor and raw materials that go into producing a product. Since operating income takes into account operating costs (i.e. COGS and OpEx), it represents the cash flow from core operations before accounting for other non-core sources of income/expenses. Examples of operating costs includes repairs, salaries, supplies, and rent.
Accountants sometimes remove non-operating expenses to examine the performance of the business, ignoring the effects of financing and other irrelevant issues. It is entirely possible for a company to be running a sound operation and still incur unusual expenses that aren’t likely to recur. When you separate operating and non-operating expenses on the income statement, it allows managers and investors to better assess the actual performance of a business. Operating and non-operating expenses are listed in different sections of a firm’s income statement.
Capital expenditures are typically for fixed assets like property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). For example, if an oil company buys a new drilling rig, the transaction would be a capital expenditure. A non-operating expense is an expense incurred by a business that is unrelated to its core operations. All operating costs will need paying, regardless of whether the store is open or closed.
Income Statement – Also known as Profit & loss statement, this financial statement focuses on the revenues (operating and non-operating), expenses , gains, and losses. Operating expenses along with expenses incurred from production of the product are recorded under primary activity expenses. The definition of operating expenses is any expense that is not directly related to producing goods that are sold. Non-operating expenses include any expenses that are directly related to producing goods that are sold, or COGS.
Electrical power costs are the major operating expense for many power-intensive processes, such as air separation plants.
Capital expenses are costs firms incur while making an investment. For instance, they may upgrade some equipment or acquire a patent for new VoIP technology. These are expenses businesses choose to take on in the hope of getting a return on investment down the road. By keeping a close eye on operating expenses, finance teams can identify outliers and trends that could reveal opportunities to reduce expenses without sacrificing product or service quality.
Examples of CapEx include physical assets, such as buildings, equipment, machinery, and vehicles. Depreciation is an accounting method of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life to account for declines in value over time. Harold Averkamp has worked as a university accounting instructor, accountant, and consultant for more than 25 years. He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com.

Less common non-operating expenses can also include inventory write-offs, restructuring costs and even settlements for lawsuits. An operating expense is any expense needed to keep a business running that is not directly related to the production of goods sold. Operating expenses are important for keeping track of costs so that management and investors can properly determine if a business is running properly and keep the business running.
Some business expenditures are incurred for reasons that don’t involve normal business operations. For instance, the costs of relocating your business falls outside core business operations and would be recorded as a non-operating expense. Another example of a non-operating expense is interest on borrowed money. Operating expenses are the costs that have been used up as part of a company’s main operating activities during the period shown in the heading of its income statement. There may be more such expenses depending on the nature of the store’s business. Operating costs may add up to a hefty total and the storeowner should consider all operating expenses before going into business.

